Who Should Use This Tool?
Cain & Abel is a tool that will be quite useful for network administrators, teachers, professional penetration testers, security consultants/professionals, forensic staff and security software vendors.
Requirements
The system requirements needed to successfully setup Cain & Abel are:
– At least 10MB hard disk space
– Microsoft Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista OS
– Winpcap Packet Driver (v2.3 or above).
– Airpcap Packet Driver (for passive wireless sniffer / WEP cracker).
Installation
First we need to download Cain & Abel, so go to the download page www.oxid.it/cain.html.
After downloading it,just run the Self-Installing executable package and follow the installation instructions.
Cain’s Features
Here’s a list of all of Cain’s features that make it a great tool for network penetration testing:
Related Definitions:
MAC: (from Wikipedia) “A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies, including Ethernet. Logically, MAC addresses are used in the Media Access Control protocol sub-layer of the OSI reference model.
MAC addresses are most often assigned by the manufacturer of a network interface card (NIC) and are stored in its hardware, the card’s read-only memory, or some other firmware mechanism. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer’s registered identification number and may be referred to as the burned-in address. It may also be known as an Ethernet hardware address (EHA), hardware address or physical address. A network node may have multiple NICs and will then have one unique MAC address per NIC.”
Sniffing: (fromWikipedia) “A packet analyzer (also known as a network analyzer, protocol analyzer or packet sniffer, or for particular types of networks, an Ethernet sniffer or wireless sniffer) is a computer program or a piece of computer hardware that can intercept and log traffic passing over a digital network or part of a network. As data streams flow across the network, the sniffer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet’s raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications.”
ARP(from Wikipedia) “Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a telecommunications protocol used for resolution of network layer addresses into link layer addresses, a critical function in multiple-access networks. ARP was defined by RFC 826 in 1982. It is Internet Standard STD 37. It is also the name of the program for manipulating these addresses in most operating systems.”
Usage
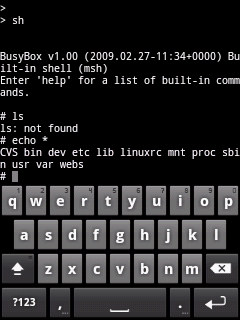
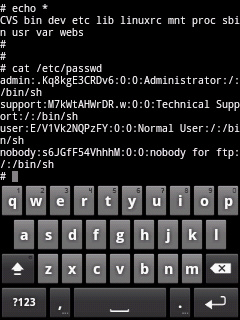
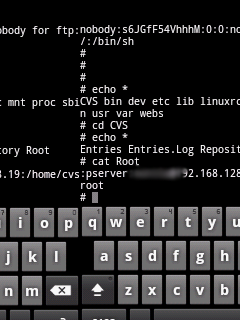
Now after launching the application, we have to configure it to use appropriate network card.If you have multiple network cards, it’s better to know the MAC address of the network card that you will use for the sniffer.To get the MAC address of your network interface card, do the following:

Now let’s go through the configuration dialog tabs and take a brief look at most of them:
Sniffer Tab:
This tab allows us to specify which Ethernet interface card we will use for sniffing.
There are some features of Cain that parse information from web pages viewed by the victim such as LSA Secrets dumper, HTTP Sniffer and ARP-HTTPS,so the more fields you add to the username and passwords fields, the more you capture HTTP usernames and passwords from HTTP and HTTPS requests. Here is an example:
The following cookie uses the fields “logonusername=” and “userpassword=” for authentication purposes. If you don’t include these two fields in the list, the sniffer will not extract relative credentials.
GET /mail/Login?domain=xxxxxx.xx&style=default&plain=0 HTTP/1.1
Accept: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, application/x-shockwave-flash, */*
Referer: http://xxx.xxxxxxx.xx/xxxxx/xxxx
Accept-Language: it
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1; (R1 1.3); .NET CLR 1.1.4322)
Host: xxx.xxxxxx.xx
Connection: Keep-Alive
Cookie: ss=1; logonusername=user@xxxxxx.xx; ss=1; srclng=it; srcdmn=it; srctrg=_blank; srcbld=y; srcauto=on; srcclp=on; srcsct=web; userpassword=password; video=c1; TEMPLATE=default;
Traceroute Tab:
Traceroute is a technique to determine the path between two points by simply counting how many hops the packet will take from the source machine to reach the destination machine. Cain also adds more functionality that allows hostname resolution, Net mask resolution, and Whois information gathering.
Certificate Spoofing Tab:
This tab will allow Certificate spoofing.From Wikipedia:
“In cryptography, a public key certificate (also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate) is an electronic document that uses a digital signature to bind a public key with an identity — information such as the name of a person or an organization, their address, and so forth. The certificate can be used to verify that a public key belongs to an individual.
In a typical public key infrastructure (PKI) scheme, the signature will be of a certificate authority (CA). In a web of trust scheme, the signature is of either the user (a self-signed certificate) or other users (“endorsements”). In either case, the signatures on a certificate are attestations by the certificate signer that the identity information and the public key belong together.”
We can simply think of it as some sort of data (cipher suites & Public key and some other information about the owner of the certificate) that has information about the destination server and is encrypted by trusted companies (CA) that are authorized for creating these types of data.The server sends its own certificate to the client application to make sure it’s talking to the right server.
Certificate Collector Tab:
This tab will collect all certificates back and forth between servers and clients by setting proxy IPs and ports that listen to it.
Password Cracking
Now it’s time to speak about the cracker tab,the most important feature of Cain.When Cain captures some LM and NTLM hashes or any kind of passwords for any supported protocols, Cain sends them automatically to the Cracker tab.We will import a local SAM file just for demonstration purposes to illustrate this point.Here is how to import the SAM file:

Here are the 4 NTLM and LM hashes which will appear like the following image:

And here you will find all possible password techniques in the following image:

As you can see from the previous image, there are various types of techniques that are very effective in password cracking.We will look at each of their definitions.
Cain & Abel is a tool that will be quite useful for network administrators, teachers, professional penetration testers, security consultants/professionals, forensic staff and security software vendors.
Requirements
The system requirements needed to successfully setup Cain & Abel are:
– At least 10MB hard disk space
– Microsoft Windows 2000/XP/2003/Vista OS
– Winpcap Packet Driver (v2.3 or above).
– Airpcap Packet Driver (for passive wireless sniffer / WEP cracker).
Installation
First we need to download Cain & Abel, so go to the download page www.oxid.it/cain.html.
After downloading it,just run the Self-Installing executable package and follow the installation instructions.
Cain’s Features
Here’s a list of all of Cain’s features that make it a great tool for network penetration testing:
| Protected Storage Password Manager | Credential Manager Password Decoder |
| LSA Secrets Dumper | Dialup Password Decoder |
| Service Manager | APR (ARP Poison Routing) |
| Route Table Manager | Network Enumerator |
| SID Scanner | Remote Registry |
| Sniffer | Routing Protocol Monitors |
| Full RDP sessions sniffer for APR | Full SSH-1 sessions sniffer for APR |
| Full HTTPS sessions sniffer for APR | Full FTPS sessions sniffer for APR |
| Full POP3S sessions sniffer for APR | Full IMAPS sessions sniffer for APR |
| Full LDAPS sessions sniffer for APR | Certificates Collector |
| MAC Address Scanner with OUI fingerprint | Promiscuous-mode Scanner |
| Wireless Scanner | PWL Cached Password Decoder |
| 802.11 Capture Files Decoder | Password Crackers |
| Access (9x/2000/XP) Database Passwords Decoder | Cryptanalysis attacks |
| Base64 Password Decoder | WEP Cracker |
| Cisco Type-7 Password Decoder | Rainbowcrack-online client |
| Cisco VPN Client Password Decoder | Enterprise Manager Password Decoder |
| RSA SecurID Token Calculator | Hash Calculator |
| TCP/UDP Table Viewer | TCP/UDP/ICMP Traceroute |
| Cisco Config Downloader/Uploader (SNMP/TFTP) | Box Revealer |
| Wireless Zero Configuration Password Dumper | Remote Desktop Password Decoder |
| MSCACHE Hashes Dumper | MySQL Password Extractor |
| Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Password Extractor | Oracle Password Extractor |
| VNC Password Decoder | Syskey Decoder |
MAC: (from Wikipedia) “A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies, including Ethernet. Logically, MAC addresses are used in the Media Access Control protocol sub-layer of the OSI reference model.
MAC addresses are most often assigned by the manufacturer of a network interface card (NIC) and are stored in its hardware, the card’s read-only memory, or some other firmware mechanism. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer’s registered identification number and may be referred to as the burned-in address. It may also be known as an Ethernet hardware address (EHA), hardware address or physical address. A network node may have multiple NICs and will then have one unique MAC address per NIC.”
Sniffing: (fromWikipedia) “A packet analyzer (also known as a network analyzer, protocol analyzer or packet sniffer, or for particular types of networks, an Ethernet sniffer or wireless sniffer) is a computer program or a piece of computer hardware that can intercept and log traffic passing over a digital network or part of a network. As data streams flow across the network, the sniffer captures each packet and, if needed, decodes the packet’s raw data, showing the values of various fields in the packet, and analyzes its content according to the appropriate RFC or other specifications.”
ARP(from Wikipedia) “Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a telecommunications protocol used for resolution of network layer addresses into link layer addresses, a critical function in multiple-access networks. ARP was defined by RFC 826 in 1982. It is Internet Standard STD 37. It is also the name of the program for manipulating these addresses in most operating systems.”
Usage
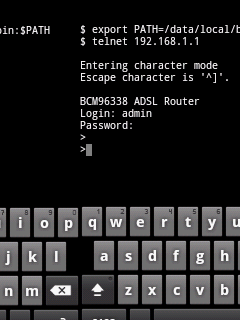
Now after launching the application, we have to configure it to use appropriate network card.If you have multiple network cards, it’s better to know the MAC address of the network card that you will use for the sniffer.To get the MAC address of your network interface card, do the following:
1- Open CMD prompt.
/p>
/p>
2- Write the following command “ipconfig /all”.
3- Determine the MAC address of the
desired Ethernet adapters, write it on Notepad,and then use this
information to help determine which NIC to select in the Cain
application.
Now clickConfigure on the main menu.
It will open the configuration dialog box where you can select the
desired network interface card.

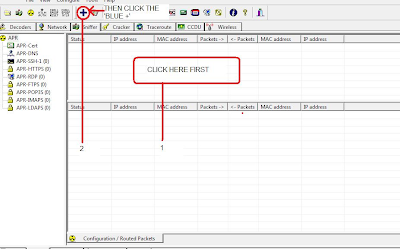
Sniffer Tab:
This tab allows us to specify which Ethernet interface card we will use for sniffing.
ARP Tab:
This tab allows us to configure ARP
poison routing to perform ARP poisoning attack, which tricks the
victim’s computer by impersonating other devices to get all traffic that
belongs to that device, which is usually the router or an important
server.
Filters and Ports Tab:
This tab has the most standard
services with their default port running on.You can change the port by
right-clicking on the service whose port you want to change and then
enabling or disabling it.
Cain’s sniffer filters and application protocol TCP/UDP port.
HTTP Fields Tab:There are some features of Cain that parse information from web pages viewed by the victim such as LSA Secrets dumper, HTTP Sniffer and ARP-HTTPS,so the more fields you add to the username and passwords fields, the more you capture HTTP usernames and passwords from HTTP and HTTPS requests. Here is an example:
The following cookie uses the fields “logonusername=” and “userpassword=” for authentication purposes. If you don’t include these two fields in the list, the sniffer will not extract relative credentials.
GET /mail/Login?domain=xxxxxx.xx&style=default&plain=0 HTTP/1.1
Accept: image/gif, image/x-xbitmap, image/jpeg, image/pjpeg, application/vnd.ms-excel, application/vnd.ms-powerpoint, application/msword, application/x-shockwave-flash, */*
Referer: http://xxx.xxxxxxx.xx/xxxxx/xxxx
Accept-Language: it
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1; SV1; (R1 1.3); .NET CLR 1.1.4322)
Host: xxx.xxxxxx.xx
Connection: Keep-Alive
Cookie: ss=1; logonusername=user@xxxxxx.xx; ss=1; srclng=it; srcdmn=it; srctrg=_blank; srcbld=y; srcauto=on; srcclp=on; srcsct=web; userpassword=password; video=c1; TEMPLATE=default;
Traceroute Tab:
Traceroute is a technique to determine the path between two points by simply counting how many hops the packet will take from the source machine to reach the destination machine. Cain also adds more functionality that allows hostname resolution, Net mask resolution, and Whois information gathering.
Certificate Spoofing Tab:
This tab will allow Certificate spoofing.From Wikipedia:
“In cryptography, a public key certificate (also known as a digital certificate or identity certificate) is an electronic document that uses a digital signature to bind a public key with an identity — information such as the name of a person or an organization, their address, and so forth. The certificate can be used to verify that a public key belongs to an individual.
In a typical public key infrastructure (PKI) scheme, the signature will be of a certificate authority (CA). In a web of trust scheme, the signature is of either the user (a self-signed certificate) or other users (“endorsements”). In either case, the signatures on a certificate are attestations by the certificate signer that the identity information and the public key belong together.”
We can simply think of it as some sort of data (cipher suites & Public key and some other information about the owner of the certificate) that has information about the destination server and is encrypted by trusted companies (CA) that are authorized for creating these types of data.The server sends its own certificate to the client application to make sure it’s talking to the right server.
Certificate Collector Tab:
This tab will collect all certificates back and forth between servers and clients by setting proxy IPs and ports that listen to it.
Challenge Spoofing Tab:
Here you can set the custom challenge value to rewrite into NTLM authentications packets. This feature can be enabled quickly from Cain’s toolbar and must be used with APR. A fixed challenge enables cracking of NTLM hashes captured on the network by means of Rainbow Tables.Password Cracking
Now it’s time to speak about the cracker tab,the most important feature of Cain.When Cain captures some LM and NTLM hashes or any kind of passwords for any supported protocols, Cain sends them automatically to the Cracker tab.We will import a local SAM file just for demonstration purposes to illustrate this point.Here is how to import the SAM file:

Here are the 4 NTLM and LM hashes which will appear like the following image:

And here you will find all possible password techniques in the following image:

As you can see from the previous image, there are various types of techniques that are very effective in password cracking.We will look at each of their definitions.